The branch of scientific computing, modeling and simulation comprises the creation and use of algorithms and mathematical computational models that facilitate the study of phenomena in different areas of science and engineering, as an alternative to analysis by direct experimentation. The projects that are developed involve the study of large-scale or complex systems, where high computing capacity is required to perform realistic calculations and simulations. At the CNCA, we work together with professionals in meteorology, chemistry, physics, environmental sciences, among others, who seek to rely on these computational tools to solve their scientific problems. This branch also has the Scientific Computing Research Network (RICC), a network of collaborators in the research area whose work is related to scientific computing.
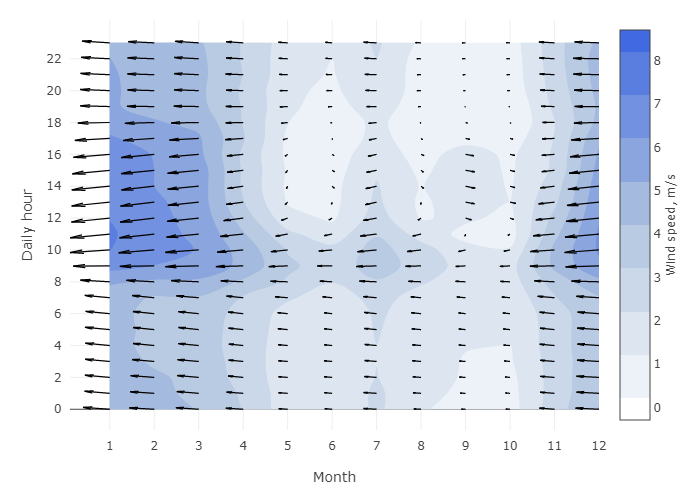
Climate and factors that affect their behavior are topics that have become increasingly relevant in research, given their anthropogenic contribution to climate change and global warming. The consequences of air pollution are diverse, even for human activities. Such is the case analyzed in the Atmospheric Pollutants Transport project in the Western Central Valley, which aims at observing the distribution of pollutants in the atmosphere and assessing their impact on man-made metal structures. The CNCA has collaborated in this project with experts from different areas in analysis and calculation using data from meteorological stations distributed throughout the Central Valley, to generate predictive models of metal corrosion based on meteorological variables. Also, it has contributed to the use of complex climate prediction programs such as the Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) to describe the distribution of these pollutants and the behavior of other variables such as winds, temperature, rainfall, and relative humidity. This type of research requires using scientific computing and machine learning modules in Python language, in addition to working with climate models implemented in C and Fortran, whose execution has demanded the use of high-performance computing.
Transportation of Air Pollutants in the Western Central Valley